Microscope Lab: Comparing Monocot and Dicots
Title: Root and Stems
Purpose: Students are to make their own
Materials: Students are to make their own
Procedures:
PART A:
1. Examine the slide of the root
2. Make a detailed sketch of the root and label the parts i) cortex, epidermis, endodermis, root hairs, vascular cylinder.
3. This is to be done under low power magnification (40x) for the monocot and dicot specimens provided on the slide.
PART B:
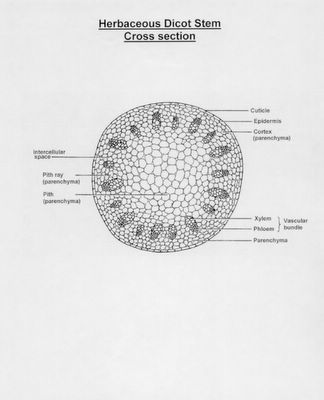
4. Examine the slide of the stem
5. Make a detailed sketch of the stem and label the parts.
6. This is to be done under low or medium power magnification. To make sure that you do not have to draw the entire field of view. Simply draw a slice of a circle (field of view) and draw that out. Make sure to state the magnification of your drawing.
7. Using the high power magnification sketch a detailed picture of the vascular bundle in both the monocot and dicot stems. Clearly label each part of the vascular bundle.
Discussion:
Using a chart format summarize each cell type, function, and location in both the monocot and dicot plant. This is to be done for both the root and the stem.
This lab will be due on Wednesday March 30th.